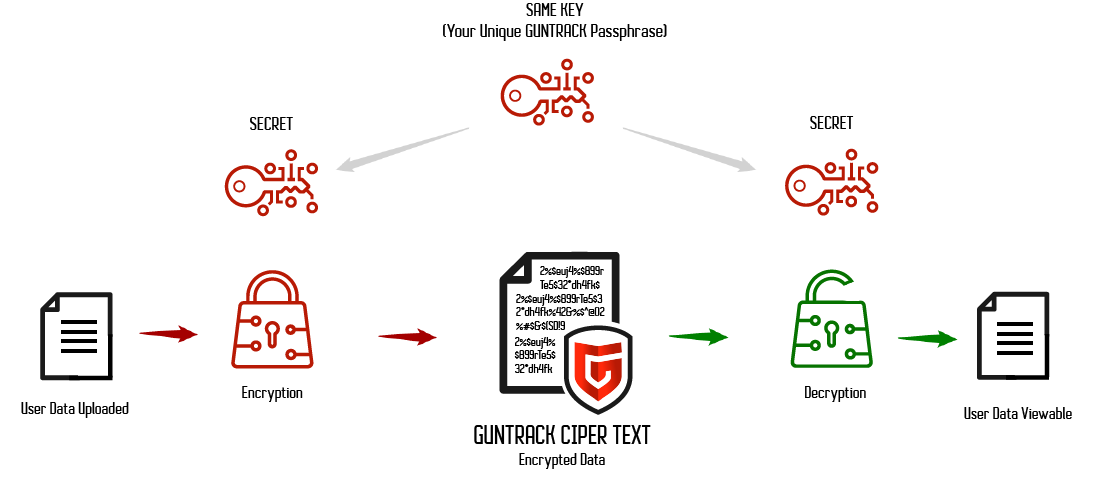
Today AES 256-bit encryption is the most robust encryption standard available. The Advanced Encryption System (AES) is the current encryption standard chosen by the U.S. government since 2001. It’s quickly become the encryption standard for most private sector enterprises. AES is also the first publicly available cipher approved by the U.S. National Security Agency (NSA) to protect top-secret information. AES was first known as Rijndael, named after its two developers, Belgian cryptographers Vincent Rijmen and Joan Daemen.

AES-256 is practically unbreakable
AES-256 has a key length of 256 bits, which supports the largest bit size and is unbreakable by brute force. This means it would take the fastest computer in the world millions if not billions of years to crack. Here are the possible combinations:
| Key Size | Possible Combinations |
| 1 bit | 2 |
| 2 bits | 4 |
| 4 bits | 16 |
| 8 bits | 256 |
| 16 bits | 65536 |
| 32 bits | 4.2 x 109 |
| 56 bits (DES) | 7.2 x 1016 |
| 64 bits | 1.8 x 1019 |
| 128 bits (AES) | 3.4 x 1038 |
| 192 bits (AES) | 6.2 x 1057 |
| 256 bits (AES) | 1.1 x 1077 |